A new World Bank reports finds that water scarcity, exacerbated by climate change, could hinder economic growth, spur migration, and spark conflict.
The report adds however that most countries can neutralise the adverse impacts of water scarcity by taking action to allocate and use water resources more efficiently.
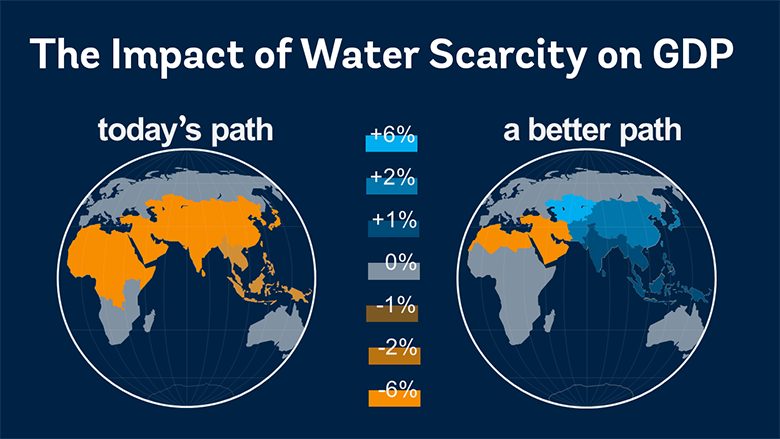
According to the report, climate change influenced-water scarcity could cost some regions up to 6% of their gross domestic product (GDP).
The combined effects of growing populations, rising incomes, and expanding cities, notes the report, will see demand for water rising exponentially, while supply becomes more erratic and uncertain.
The study warns that, unless action is taken soon, water will become scarce in regions where it is currently abundant – such as Central Africa and East Asia – and scarcity will greatly worsen in regions where water is already in short supply – such as the Middle East and the Sahel in Africa.
These regions, stresses the report, could see their growth rates decline by as much as 6% of GDP by 2050 due to water-related impacts on agriculture, health, and incomes.
Water insecurity could multiply the risk of conflict, says the report, adding that food price spikes caused by droughts can inflame latent conflicts and drive migration.
“Where economic growth is impacted by rainfall, episodes of droughts and floods have generated waves of migration and spikes in violence within countries.
“The negative impacts of climate change on water could be neutralised with better policy decisions, with some regions standing to improve their growth rates by up to 6% with better water resource management,” the report finds.
Some of the report’s other key findings include:
- Improved water stewardship pays high economic dividends. When governments respond to water shortages by boosting efficiency and allocating even 25% of water to more highly-valued uses, such as more efficient agricultural practices, losses decline dramatically and for some regions may even vanish.
- In the world’s extremely dry regions, more far-reaching policies are needed to avoid inefficient water use. Stronger policies and reforms are needed to cope with deepening climate stresses.
- Policies and investments that can help lead countries to more water secure and climate-resilient economies include:
(1) Better planning for water resource allocation;
(2) Adoption of incentives to increase water efficiency, and
(3) Investments in infrastructure for more secure water supplies and availability.
