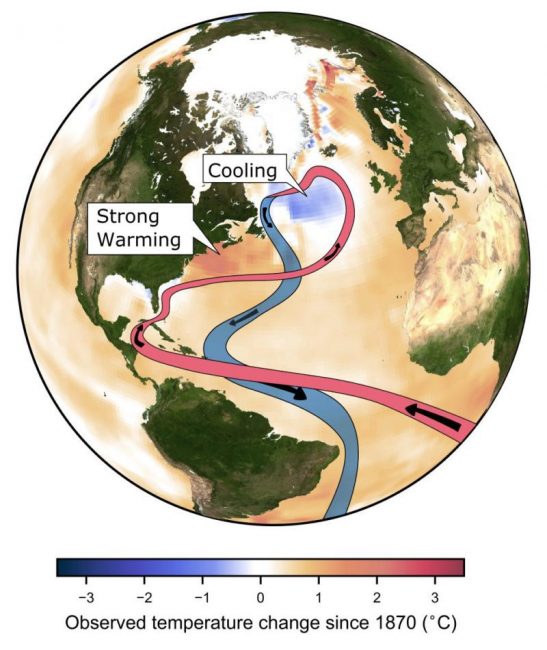
The Atlantic overturning – one of Earth’s most important heat transport systems, pumping warm water northwards and cold water southwards – is weaker today than any time before in more than 1,000 years.
Sea surface temperature data analysis provides new evidence that this major ocean circulation has slowed down by roughly 15 percent since the middle of the 20th century, according to a study published in the highly renowned journal Nature by an international team of scientists. Human-made climate change is said to be a prime suspect for the worrying observations.
“We detected a specific pattern of ocean cooling south of Greenland and unusual warming off the US coast – which is highly characteristic for a slowdown of the Atlantic overturning, also called the Gulf Stream System,” says lead-author Levke Caesar from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). “It is practically like a fingerprint of a weakening of these ocean currents.” As the currents slow down, they bring less heat towards the north, causing widespread cooling of the northern Atlantic – the only ocean region that has cooled in the face of global warming. At the same time, the Gulf Stream shifts northwards and closer to shore and warms the waters along the northern half of the US Atlantic coast.
“That region has warmed faster than most other parts of the world ocean in recent decades,” says co-author Vincent Saba from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Laboratory in Princeton, USA. “This specific ocean temperature pattern has been projected by high-resolution computer simulations as a response to rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere – now it has been confirmed by measurements.”
Measurements of sea surface temperatures confirm computer simulations
For decades, scientists have investigated the dynamics of the Atlantic overturning. Computer simulations generally predict that it will weaken in response to human-caused global warming. But whether this is already happening has so far been unclear, due to a lack of long-term direct current measurements. “The evidence we’re now able to provide is the most robust to date,” says Stefan Rahmstorf from the Potsdam Institute, who conceived the study. “We’ve analysed all the available sea surface temperature data sets, comprising data from the late 19th Century until the present.”
“The specific trend pattern we found in measurements looks exactly like what is predicted by computer simulations as a result of a slowdown in the Gulf Stream System, and I see no other plausible explanation for it,” says Rahmstorf. It is in fact not just the pattern in space that matches between computer simulation and observations, but also the change with the seasons.
Global warming likely causes the changes – the effects are far-reaching
The weakening is caused by a number of factors that can be linked to global warming which is caused by greenhouse gases from burning coal, oil, and gas. The Atlantic overturning is driven by the differences in the density of the ocean water: when the warm and hence lighter water travels from the South to the North, it becomes colder and thereby denser and heavier – making it sink to deeper ocean layers and flow back to the south. “But with global warming, increased rainfall as well as meltwater from the Arctic sea ice and Greenland ice sheet is diluting the waters of the northern Atlantic, reducing the salinity. Less saline water is less dense and hence less heavy – which makes it harder for the water to sink from the surface into the deep,” explains Alexander Robinson of the University of Madrid, who co-authored the study.
There have been long debates whether the Atlantic overturning could collapse, being a tipping element in the Earth system. The present study does not consider the future fate of this circulation, but rather analyses how it has changed over the past hundred years. Nevertheless, Robinson cautions: “If we do not rapidly stop global warming, we must expect a further long-term slowdown of the Atlantic overturning. We are only beginning to understand the consequences of this unprecedented process – but they might be disruptive.”
Several studies have shown, for example, that a slowdown of the Atlantic overturning exacerbates sea-level rise on the US coast for cities like New York and Boston. Others show that the associated change in Atlantic sea surface temperatures affects weather patterns over Europe, such as the track of storms coming off the Atlantic. Specifically, the European heat wave of summer 2015 has been linked to the record cold in the northern Atlantic in that year – this seemingly paradoxical effect occurs because a cold northern Atlantic promotes an air pressure pattern that funnels warm air from the south into Europe.