At least 1.4 million people uprooted by Boko Haram’s insurgency in northeast Nigeria are living in “cholera hotspot”’, prey to an outbreak of the deadly disease which is sweeping through camps for the displaced, the United Nations said on Thursday, September 7, 2017.
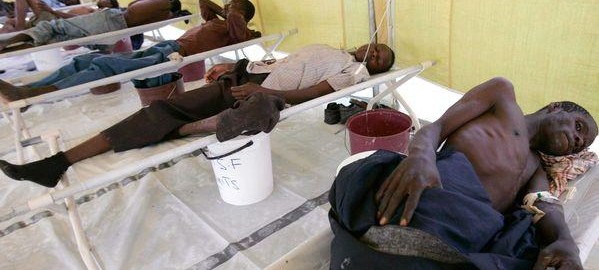
An estimated 28 people have died from cholera in the conflict-hit region, while about 837 are suspected to have been infected with the disease, including at least 145 children under the age of five, said the U.N. children’s agency, UNICEF.
The outbreak was first identified last week in the Muna Garage camp in Maiduguri, the capital of Borno state, which is the heart of jihadist group Boko Haram’s brutal eight-year campaign to carve out an Islamic caliphate in northeast Nigeria.
About 1.8 million people have abandoned their homes because of violence or food shortages, U.N. agencies say, and many live in camps for the displaced throughout northeast Nigeria.
Several aid agencies last month told the Thomson Reuters Foundation that Nigeria’s rainy season could spread disease in already unsanitary displacement camps, and 350,000 uprooted children aged under five are at risk of cholera, UNICEF said.
“Cholera is difficult for young children to withstand at any time, but becomes a crisis for survival when their resilience is already weakened by malnutrition, malaria and other waterborne diseases,” UNICEF’s Pernille Ironside said in a statement.
“Cholera is one more threat amongst many that children in northeast Nigeria are battling today in order to survive,” added Ironside, UNICEF’s deputy representative in Nigeria.
UNICEF said aid agencies have set up a cholera treatment centre at the Muna Garage camp, chlorinated water in camps and host communities to curb the outbreak, and mobilised volunteers and local leaders to refer suspected cases to health facilities.
The disease, which spreads through contaminated food and drinking water, causes diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. It can kill within hours if left untreated, but most patients recover if treated promptly with oral rehydration salts.
The latest figures represent a 3.3 percent fatality rate – well above the 1 percent rate that the World Health Organisation (WHO) rates as an emergency. The short incubation period of two hours to five days means the disease can spread with explosive speed.
More than 20,000 people have been killed in the conflict with Boko Haram, at least 2.2 million have been displaced, and 5.2 million in the northeast are short of food, with tens of thousands living in famine-like conditions, U.N. figures show.
Courtesy: Thomson Reuters Foundation
